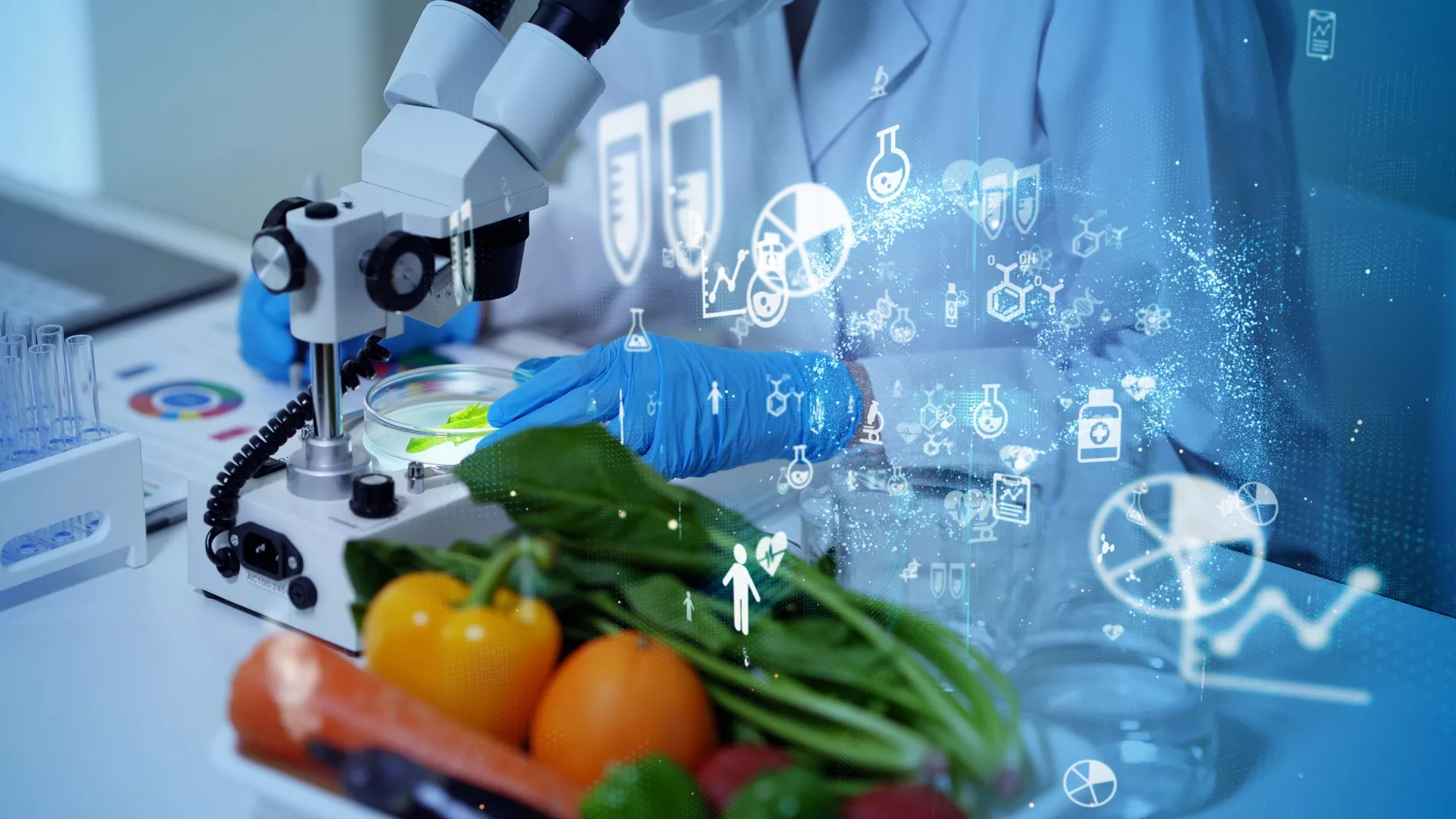
Biotechnology, a groundbreaking interdisciplinary field, has been transforming industries and revolutionizing the way we approach scientific advancements. From healthcare to agriculture and environmental conservation, biotechnology’s applications have become increasingly prominent in the current scenario.
In this blog post, we will delve into the vast array of uses and benefits of biotechnology, examining its contributions to human welfare, sustainability, and economic growth. By exploring various subfields and real-world examples, we will gain an understanding of how biotechnology has become an indispensable tool in shaping our future.
Understanding Biotechnology: A Brief Overview
Biotechnology is the utilization of biological systems, organisms, or derivatives to develop innovative solutions that improve our lives. It encompasses various subfields, including medical biotechnology, agricultural biotechnology, industrial biotechnology, and environmental biotechnology. Each of these areas plays a significant role in addressing diverse challenges and enhancing our overall quality of life.
Also Read: Tips for Creating Strategic Business Goals
Medical Biotechnology: Advancements in Healthcare
Pharmaceutical Innovations:
Medical biotechnology has revolutionized drug discovery and development. By harnessing the power of biologically active molecules, such as proteins and antibodies, biotechnology has enabled the creation of targeted therapies for a wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and rare genetic conditions. Monoclonal antibodies and gene therapies stand as prime examples of biotechnological achievements that have saved countless lives and improved patient outcomes.
Personalized Medicine:
The emergence of personalized medicine, a subset of medical biotechnology, has transformed healthcare practices. Through genetic testing and analysis, doctors can now tailor treatment plans based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup. This approach maximizes treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects, marking a significant step towards patient-centric care.
Vaccines and Infectious Disease Management:
Biotechnology has played a pivotal role in vaccine development, leading to the creation of highly effective vaccines against previously deadly infectious diseases. Recent examples, such as the rapid development of mRNA-based vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic, demonstrate biotechnology’s agility and adaptability in tackling global health crises.
Agricultural Biotechnology: Enhancing Crop Yield and Quality
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs):
Agricultural biotechnology has introduced genetically modified crops that possess improved resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental stressors. GMOs have the potential to boost agricultural productivity, reduce the need for harmful pesticides, and improve food security in a world facing population growth and climate change challenges.
Precision Agriculture:
Biotechnology is transforming traditional farming practices through precision agriculture. By integrating data-driven technologies, such as sensors, drones, and GPS-guided machinery, farmers can optimize resource utilization, leading to increased yields, reduced costs, and minimized environmental impact.
Sustainable Agriculture:
Biotechnology offers solutions for sustainable agriculture, including the development of biofertilizers, biopesticides, and drought-resistant crops. These innovations promote eco-friendly farming practices, conserve natural resources, and protect biodiversity.
Also Read:5 Ways Soy Foods Can Improve Your Overall Health
Industrial Biotechnology: Eco-Friendly Manufacturing and Beyond
Bio-based Products:
Industrial biotechnology harnesses microorganisms and enzymes to produce bio-based materials, chemicals, and fuels. Bio-plastics, biofuels, and biodegradable products are examples of sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil-fuel-derived materials, contributing to the transition towards a more circular economy.
Bioremediation:
Biotechnology plays a crucial role in bioremediation, a process that uses living organisms to remove or neutralize pollutants from the environment. This approach has been successfully applied to clean up contaminated sites and restore ecosystems affected by human activities.
Environmental Biotechnology: Conservation and Restoration
Waste Management:
Environmental biotechnology offers innovative solutions for waste management, including the conversion of organic waste into biogas through anaerobic digestion. This process not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also generates renewable energy.
Conservation Efforts:
Biotechnology aids conservation efforts through genetic analysis, helping scientists understand and preserve endangered species. In-vitro fertilization and cryopreservation techniques have been employed to conserve genetic diversity and revive threatened animal populations.
Conclusion:
Biotechnology has become an indispensable and transformative force in the current scenario, shaping industries and improving human welfare. From personalized medicine to sustainable agriculture and eco-friendly manufacturing, its applications have the potential to address critical global challenges. By harnessing the power of biological systems, biotechnology continues to pave the way for a more prosperous, healthier, and sustainable future for all of humanity.
Also Read: How to Live Life With Ease – Read To Know Amazing Facts
However, it is essential to strike a balance between scientific progress and ethical considerations, ensuring that biotechnological advancements benefit society as a whole. As we embrace the potential of biotechnology, responsible stewardship and collaboration among governments, scientists, and stakeholders will be key in maximizing its usefulness while addressing any ethical concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is biotechnology safe for the environment?
Yes, biotechnology can be environmentally friendly when applied responsibly. By promoting sustainable practices and reducing reliance on harmful chemicals, biotechnology contributes to a cleaner and greener future.
Are genetically modified organisms (GMOs) safe for consumption?
Extensive scientific studies have consistently shown that approved GMOs are safe for consumption. Regulatory bodies rigorously assess their safety before they are introduced to the market.
Can biotechnology solve global hunger?
Biotechnology, particularly agricultural biotechnology, has the potential to play a significant role in addressing global hunger. By developing crops with improved yields and nutritional content, biotechnology can help provide sufficient food for a growing population.
Does biotechnology only benefit the developed world?
No, biotechnology has applications that can benefit both developed and developing countries. For instance, disease-resistant crops and affordable diagnostics can have a significant positive impact on agriculture and healthcare in developing regions.
Is biotechnology ethically acceptable?
The ethical implications of biotechnology are subject to ongoing debates. Ethical considerations involve issues such as genetic modification, human cloning, and the use of animals in research. Responsible governance and transparent dialogue are essential to address these concerns appropriately.
As the driving force behind WikiPluck, I am dedicated to curating and sharing insightful knowledge across a spectrum of subjects. From technology trends to Business advice, WikiPluck strives to be a go-to resource for those seeking to enhance their understanding and make informed decisions.
Join me on this journey of discovery and enlightenment as we pluck the gems of wisdom from the vast landscape of knowledge.